Atrial Fibrillation: Symptoms, Causes, and Treatment Options
Everything you need to know about AFib - from recognizing symptoms to understanding treatment options including medication and ablation procedures.
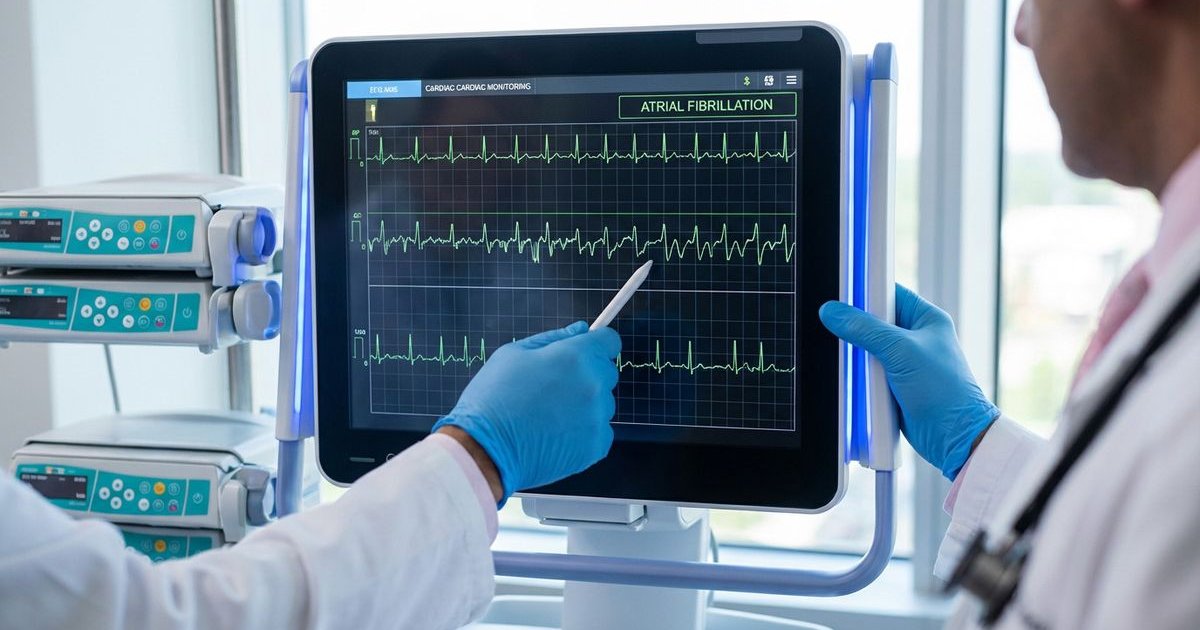
Atrial fibrillation, widely known as AFib, currently impacts an estimated 12.1 million Americans according to recent CDC projections. If you have recently received a diagnosis or suspect you are experiencing symptoms, the situation often feels overwhelming.
We see this uncertainty every day in our practice. Most people simply want to know if they can continue their normal lives and how to stop the chaotic feeling in their chest.
The good news is that management strategies have advanced significantly in the last few years. Our heart rhythm disorder specialists want to walk you through exactly what is happening in your heart and the practical steps you can take to regain control.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation?
Your heart relies on a specific electrical pathway to pump blood efficiently. In a healthy heart, the sinus node acts as a natural pacemaker. It sends an organized signal that tells the upper chambers (atria) to contract and push blood into the lower chambers (ventricles).
We often describe AFib to our patients as an “electrical storm.” During an episode, chaotic signals overwhelm the sinus node. Instead of a strong, coordinated contraction, the atria simply quiver.
This quivering prevents blood from moving effectively. The result is an irregular, often rapid heartbeat that can leave you feeling drained or anxious.
Key Insight: During AFib, the heart’s electrical rate in the upper chambers can reach 300 to 600 beats per minute. Fortunately, the AV node (the gatekeeper to the lower chambers) blocks most of these signals, but the pulse you feel is still erratic.
Types of Atrial Fibrillation
Classifying AFib is not just a labeling exercise. It dictates the specific treatment path we will recommend. The medical community categorizes these arrhythmias based on duration and how the heart responds to intervention.
We break down the four primary classifications below:
| Type | Duration & Characteristics | Typical Management Strategy |
|---|---|---|
| Paroxysmal | Stops on its own within 7 days (usually 24 hours). Symptoms are unpredictable. | ”Pill-in-the-pocket” meds or lifestyle changes. |
| Persistent | Lasts longer than 7 days. Will not stop without medical intervention. | Requires cardioversion (shock) or medication to reset. |
| Long-standing Persistent | Continuous irregularity lasting more than 12 months. | Focus shifts to long-term rate control or advanced ablation. |
| Permanent | The condition is accepted as the new normal. | Goal is managing rate and stroke risk, not restoring rhythm. |
Understanding where you fall on this spectrum helps us set realistic expectations for your recovery.
Symptoms of Atrial Fibrillation
Symptoms are surprisingly diverse. We have treated patients who felt like a fish was flopping in their chest, while others had no idea they had a heart condition until a routine physical.
The most frequently reported indicators include:
- Palpitations: A sensation of racing, fluttering, or pounding in the chest.
- Irregular Pulse: A heartbeat that feels erratic when checking your wrist or neck.
- Exhaustion: Unexplained fatigue or a sudden drop in your ability to exercise.
- Breathlessness: Shortness of breath during simple tasks like climbing stairs.
- Lightheadedness: Feeling dizzy or faint.
- Chest Pressure: Discomfort or pain in the chest area.
- Cognitive Fog: Confusion or difficulty focusing.
These signs can be deceptive. They may appear suddenly and vanish just as quickly.
Silent AFib: A Hidden Risk Many individuals experience “Silent AFib.” Clinical data suggests that about one-third of AFib patients do not feel symptoms. Despite the lack of warning signs, the risk of stroke remains the same. This makes regular check-ups vital, especially if you are over 65.
Causes and Risk Factors
AFib is rarely caused by a single factor. We look at the heart’s structure and your overall health to identify triggers.
Heart-Related Conditions
Physical changes to the heart muscle or valves create the perfect environment for AFib.
- High Blood Pressure: This is the leading driver. Uncontrolled pressure strains the atria over time.
- Coronary Artery Disease: Blockages reduce blood flow to heart tissue.
- Valve Issues: Leaky or tight valves force the heart to work harder.
- Congenital Defects: Structural issues present from birth.
- Post-Surgical Stress: Inflammation after heart surgery often triggers temporary AFib.
Lifestyle Factors
Daily habits play a massive role in both the onset and management of this condition.
- Holiday Heart Syndrome: We see a spike in cases after weekends or holidays due to binge drinking. Even moderate alcohol use is now linked to higher risks.
- Stimulants: Excessive caffeine or certain over-the-counter medications can act as triggers.
- Smoking: Nicotine is a potent stimulant that damages blood vessels.
- High-Intensity Stress: Severe physical or emotional strain releases adrenaline that can spark an episode.
Other Medical Triggers
Your heart health is connected to the rest of your body.
- Sleep Apnea: There is a 50% overlap between AFib and Obstructive Sleep Apnea. Treating apnea often improves heart rhythm.
- Thyroid Issues: An overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism) drives the heart rate up.
- Obesity: Excess weight increases pressure on the heart and inflammation.
- Chronic Kidney or Lung Disease: These conditions alter blood chemistry and oxygen levels.
Demographics
Certain groups face higher probabilities of developing AFib.
- Age: Risk jumps significantly after age 60.
- Family History: Genetics play a role in how your heart’s electricity is wired.
- Ancestry: Those of European descent show higher statistical prevalence.
Why AFib Matters: The Risks
The palpitations are uncomfortable, but the complications are what concern us most. We prioritize preventing two specific outcomes.
Stroke Risk
This is the most critical danger. When the atria quiver, they do not squeeze blood out completely. Blood pools in a small pocket called the Left Atrial Appendage (LAA).
We explain to patients that this stagnant blood can form a clot like milk curdling. If that clot breaks free, it travels directly to the brain. AFib raises your stroke risk by 500%. Strokes caused by AFib are often more severe because the clots tend to be larger, blocking major arteries in the brain.
Heart Failure Risk
A racing heart is an inefficient pump. Over months or years, a consistently high heart rate weakens the heart muscle. This condition, tachycardia-induced cardiomyopathy, can lead to fluid retention and heart failure.
The good news is that this type of heart failure is often reversible. Once we control the rate, heart function frequently recovers.
Diagnosis
Catching AFib requires documenting the rhythm while it is happening. Since the condition is often intermittent, a simple snapshot in the doctor’s office might miss it.
We utilize several technologies to capture the data we need:
- Standard 12-Lead ECG: The baseline test done in the office. It records rhythm for a few seconds.
- Zio Patch or Holter Monitor: Adhesive patches or wearable devices that record every heartbeat for 24 hours to 14 days. These are far less intrusive than older monitors.
- Event Monitor: A device you keep for weeks, pressing a button only when you feel symptoms.
- Implantable Loop Recorder: A tiny device injected under the chest skin that monitors rhythm for up to 3 years.
- Smart Wearables: Devices like the Apple Watch and Fitbit now have FDA-cleared algorithms to detect irregular rhythms. While not diagnostic tools, they are excellent for screening.
Additional Testing:
- Echocardiogram: An ultrasound to check for valve disease or blood clots.
- Sleep Study: Essential if you snore loudly or wake up gasping.
- Blood Panels: To rule out thyroid issues or electrolyte imbalances.
Treatment Options
Effective management is a three-pronged approach. We focus on preventing clots, controlling symptoms, and managing the heart rate.
1. Stroke Prevention
Protecting the brain is our non-negotiable first step.
- Direct Oral Anticoagulants (DOACs): Modern blood thinners like Eliquis (apixaban) and Xarelto (rivaroxaban) are the standard of care. They are safer and easier to manage than older drugs.
- Warfarin (Coumadin): An older medication that requires frequent blood checks and dietary restrictions. We generally reserve this for patients with mechanical heart valves.
- Watchman FLX / Amulet: For patients who cannot tolerate blood thinners, we can implant a device to physically seal off the Left Atrial Appendage where clots form.
2. Rate Control
Slowing the heart down helps you feel better and protects the muscle.
- Beta-blockers: Drugs like Metoprolol block adrenaline’s effect on the heart.
- Calcium Channel Blockers: Diltiazem is commonly used to relax the heart’s electrical conduction.
- Digoxin: An older drug used in specific heart failure cases.
3. Rhythm Control
This strategy aims to restore a normal sinus rhythm.
- Cardioversion: A controlled electrical shock delivered under sedation. It hits the “reset button” on the heart’s rhythm.
- Antiarrhythmic Drugs: Medications like Flecainide or Amiodarone help maintain normal rhythm. These require careful monitoring due to potential side effects.
- Catheter Ablation: This is the most effective long-term solution for many. We thread a catheter into the heart to scar the tissue causing the misfires.
- Pulsed Field Ablation (PFA): A major advancement in 2024. This technology uses non-thermal energy fields to target heart tissue with high precision, reducing procedure time and risk compared to traditional burning or freezing methods.
Rate Control vs. Rhythm Control
Patients often ask us which path is “better.” The answer depends entirely on your specific profile.
Recent major studies, such as the EAST-AFNET 4 trial, suggest that early rhythm control (restoring normal beats) may lead to better long-term outcomes than just controlling the speed.
You are likely a candidate for Rhythm Control if:
- You are younger or physically active.
- Your diagnosis is recent (within the last year).
- Your symptoms persist despite taking rate-control medication.
- You have heart failure caused by the arrhythmia.
We make this decision together based on your lifestyle goals and medical history.
Living with AFib
A diagnosis does not mean you have to stop doing what you love. Our patients run businesses, travel, and play sports.
Here is your checklist for successful management:
- Adherence is Key: Never skip a dose of your blood thinner. It is your safety net against stroke.
- Monitor Your Triggers: Keep a log. If a glass of red wine or a stressful Monday morning triggers episodes, you need to know.
- Manage Sleep Apnea: Using your CPAP machine every night can dramatically reduce AFib burden.
- Travel Smart: Carry a copy of your latest EKG and a medication list in your wallet.
- Stay Active: Moderate exercise is beneficial. We can help you define safe limits.
When to Seek Emergency Care
While most episodes are manageable at home, you need to know when to act fast.
Call 911 immediately if you experience:
- Crushing chest pain or pressure.
- Difficulty breathing that does not improve with rest.
- Sudden weakness, facial drooping, or slurred speech (signs of stroke).
- Loss of consciousness.
Partner with Experts
Your heart health is too important to manage alone. At Los Angeles Heart Specialists, our team includes board-certified cardiologists and electrophysiologists who specialize in heart rhythm disorders.
We leverage the latest technology, including Pulsed Field Ablation and advanced mapping systems, to design a care plan that fits your life. Contact us to schedule a consultation and develop a personalized plan for managing your atrial fibrillation.

LA Heart Specialists Team
Our team of board-certified cardiologists and medical writers provide expert insights on heart health.
Learn more about our teamRelated Articles

Coronary Artery Disease: What You Need to Know
Understanding coronary artery disease - the most common form of heart disease. Learn about causes, symptoms, diagnosis, and treatment options.
Heart Failure: Understanding Symptoms and Stages
Learn about the different stages of heart failure, warning signs to watch for, and how modern treatments can help manage this condition effectively.

Heart Palpitations: When to Worry and When to Relax
Are your heart palpitations serious? Learn to distinguish between harmless fluttering and symptoms that require immediate medical attention.
Have Questions About Your Heart Health?
Our board-certified cardiologists are here to help. Schedule a free consultation to discuss your concerns.